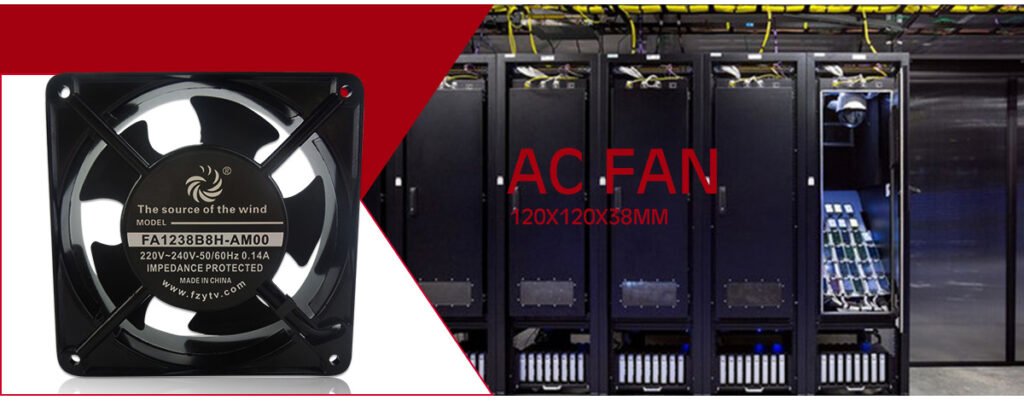
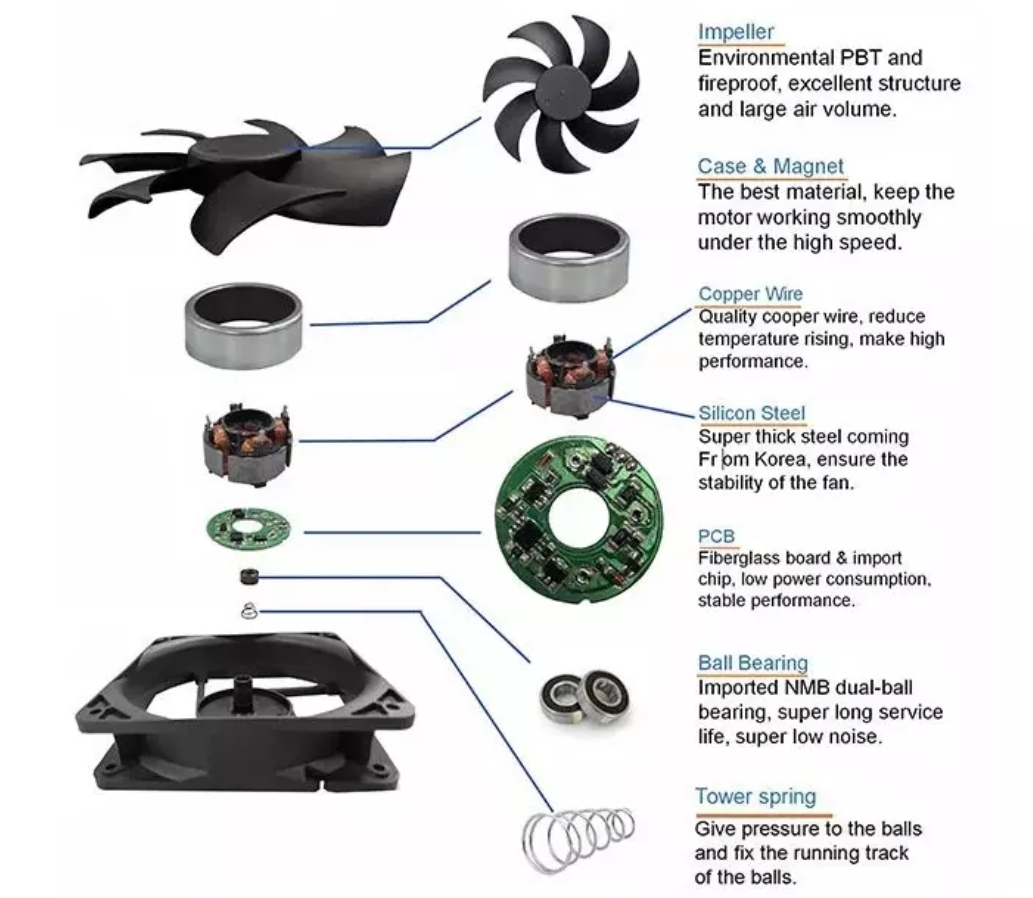
1. Look at the current of Axial Flow Fan
At the same RPM, the same voltage, the same air volume. The smaller the current, the lower the energy consumption. It is better to choose a low-current Axial flow fan.

2.Listen to the noise of Brushless Fan
The same noise, noise, noise disturbance, noise interference, because low noise is mainly related to fan blades, bearing oil, assembly structure, etc.

<1> The impeller shape design of brushless Fan will affect the air volume and the noise. This is the technical process and the ability of the self-technical personnel.
<2>The accuracy of the bearing of Fan, the smaller the friction between it and the core, the more suitable the size, the lower the noise will naturally be, which relates to the material of the bearing.
<3> Low noise of cooling Fan means that the friction is small, the life of the bearing and the shaft core will be extended, and the life of the DC Axial fan will also be maintained.
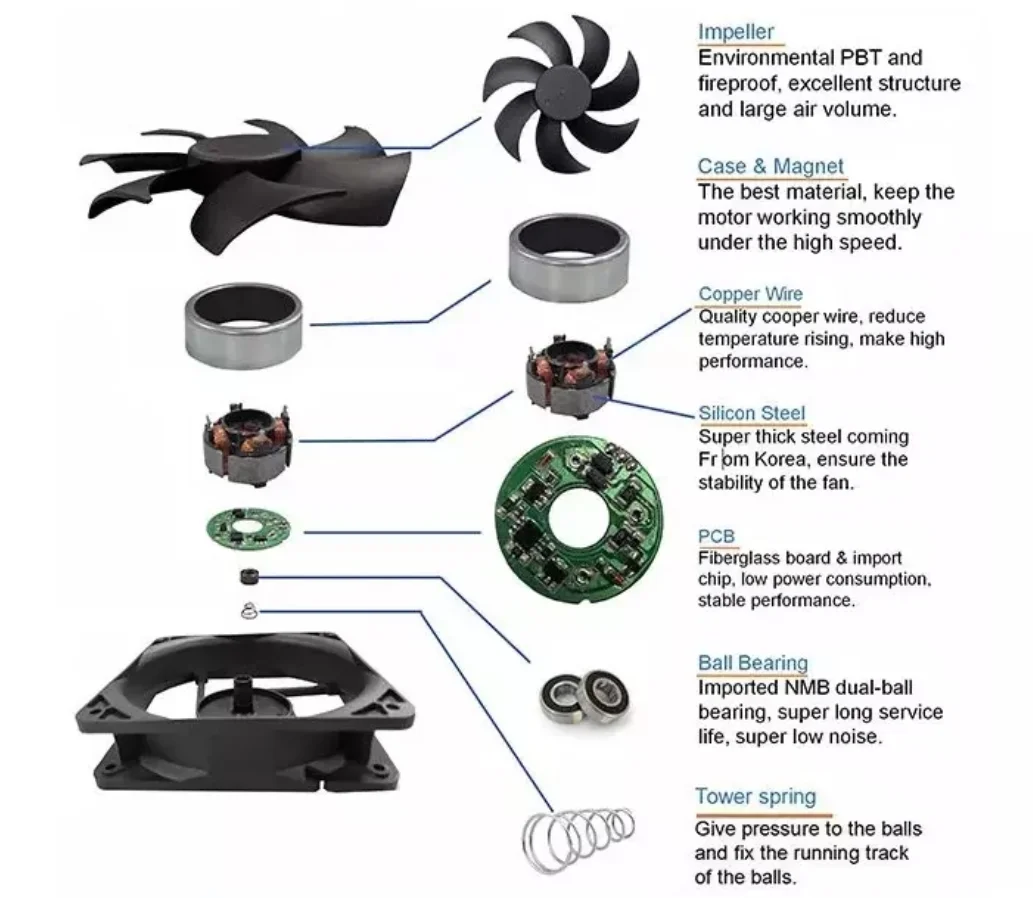
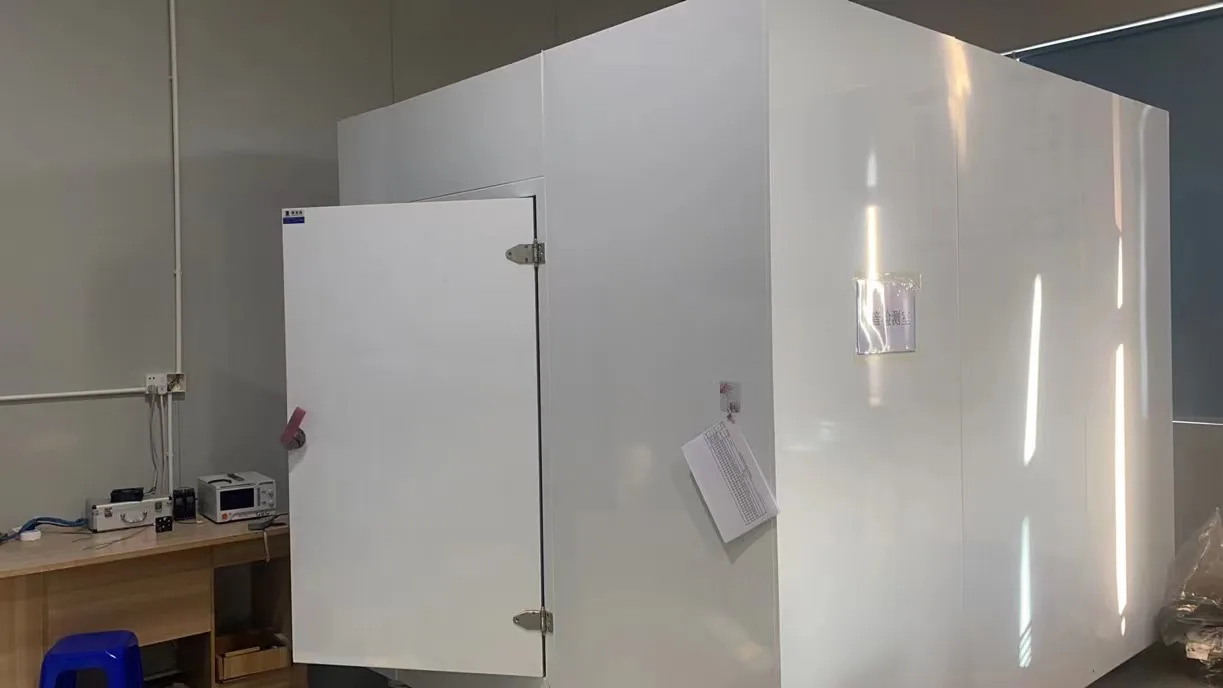
3. Vibration measurement of Axial Flow Fan
Fans with the same specifications and vibrations are better with low vibration and noise. The stronger the vibration, the performance of the fan decreases, and the consumption of the bearing and shaft core is small, and the life of the Axial Flow Fan will of course be moved.

Professional Axial Flow Fan Manufactuer
Guangzhou Mega Technology CO., LTD founded in 2008, is a manufacturer and international supply chain integrator headquartered in China. Mega manufactures a wide range of ball bearing and sleeve AC/DC axial fans, blowers and frameless fan for different applications. Low noise and extended fan life are essential for the vast majority of our customers. We offer high-quality products at competitive costs and employ flexible manufacturing techniques that enable us to respond to large and small-scale requirements. Our goal is to provide our customers with significant value-added services, ready solutions, or custom designs to meet their needs.
Besides, some of the factors to consider when selecting between these two fan designs are:
- Pressure
- Airflow rate
- Efficiency rate
- Space constraints
- Noise generation
- Drive configuration
- Operating temperature range
- Operating environment range
- Cost
- Delivery time
- Availability